In the dynamic world of fashion and apparel, sourcing decisions are pivotal. Brands constantly seek the optimal balance between cost, quality, and speed. China has long been the epicenter of clothing manufacturing, but rising costs and global shifts have prompted businesses to explore alternatives.
This article delves deep into the clothing manufacturing costs in China compared to other prominent countries, providing insights to aid in strategic sourcing decisions.
China’s Dominance in Clothing Manufacturing
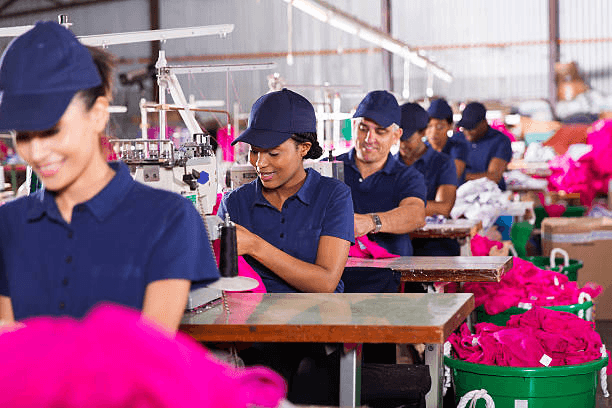

Historical Context
China’s ascent as the “world’s factory” is rooted in its vast labor force, infrastructural investments, and favorable government policies. Over the past few decades, it has established a robust supply chain ecosystem, making it a go-to destination for apparel production.
Cost Structure
- Labor Costs
While still competitive, China’s labor costs have been on the rise. As of recent data, the average manufacturing labor cost is approximately $6.50 per hour.
- Infrastructure
China boasts state-of-the-art infrastructure, ensuring efficient production and logistics.
- Economies of Scale
Large-scale operations allow for cost efficiencies, especially for bulk orders.
Advantages
- Comprehensive Supply Chain
From raw materials to finished goods, China’s integrated supply chain reduces lead times.
- Technological Advancements
The Adoption of automation and advanced manufacturing techniques enhances productivity.
Challenges
- Rising Costs
Increasing wages and operational costs are narrowing profit margins.
- Trade Tensions
Tariffs and geopolitical issues, especially with the U.S., have introduced uncertainties.
Exploring Alternative Manufacturing Hubs

Vietnam
Vietnam offers lower labor costs, averaging around $2.99 per hour, making it an attractive alternative.
- Production Capabilities
While not as expansive as China, Vietnam’s manufacturing sector is growing rapidly, with significant investments in technology and infrastructure.
- Trade Agreements
Vietnam’s participation in multiple free trade agreements provides favorable export conditions.
- Skilled Workforce
A young and increasingly skilled labor force supports diverse manufacturing needs.
- Infrastructure Gaps
While improving, certain areas still lack the infrastructural maturity seen in China.
- Supply Chain Limitations
Dependence on imported raw materials can affect lead times and costs.
India
- Labor Costs
India’s labor costs are competitive, especially in the textile sector.
- Production Capabilities
India has a vast textile industry, with strengths in cotton and handloom products.
- Diverse Product Range
From traditional garments to modern apparel, India offers a wide array of products.
- English Proficiency
Facilitates smoother communication with Western clients.
- Infrastructure Issues
Logistical challenges and infrastructural bottlenecks can impact efficiency.
- Regulatory Hurdles
Complex bureaucratic processes may pose challenges for foreign businesses.
Bangladesh
- Labor Costs
Among the lowest globally, making it a hotspot for cost-effective manufacturing.
- Production Capabilities
Specializes in the mass production of basic apparel items.
- Government Incentives
Tax breaks and favorable policies support the textile sector.
- Export Benefits
Duty-free access to major markets like the EU enhances competitiveness.
- Safety Concerns
Past incidents have raised questions about factory safety standards.
- Infrastructure Limitations
Port congestion and transportation issues can delay shipments.
Comparative Analysis
| Country | Labor Cost (per hour) | Infrastructure | Supply Chain | Trade Agreements | Safety Standards |
| China | $6.50 | Advanced | Comprehensive | Moderate | High |
| Vietnam | $2.99 | Developing | Growing | Extensive | Improving |
| India | $1.80 | Developing | Diverse | Moderate | Variable |
| Bangladesh | $1.00 | Limited | Specialized | Favorable | Concerns Exist |
Factors Influencing Manufacturing Costs
Labor Costs
Labor remains a significant component of manufacturing expenses. Countries with lower wages naturally offer cost advantages, but it’s essential to balance this with productivity and quality.
Infrastructure
Efficient transportation, reliable utilities, and advanced facilities reduce operational hiccups and ensure timely deliveries.
Supply Chain Integration
Proximity to raw materials and ancillary industries can significantly cut down costs and lead times.
Regulatory Environment
Stable political climates, transparent regulations, and supportive government policies create conducive environments for manufacturing.
Conclusion
Navigating the complex landscape of global clothing manufacturing requires a nuanced understanding of various factors. While China continues to be a dominant player, countries like Vietnam, India, and Bangladesh offer compelling alternatives, each with its unique advantages and challenges. Businesses must weigh these factors carefully, aligning them with their strategic goals, to make informed sourcing decisions.
FAQs
Which country is the cheapest to manufacture clothes?
- Economies of Scale
China’s expansive manufacturing infrastructure supports large-scale production, which significantly lowers the cost per unit. This ability to produce in bulk helps drive down overall product prices.
- Material Costs
China often benefits from easier access to raw materials, with many sourced locally. This local availability can lead to lower material costs compared to countries that rely heavily on imports.
How much import duty is on clothes from China?
BCD rate for clothes: 20%







-300x198.png)